Photo from wikipedia
Background COVID-19 is a multi-systemic disorder. Hematologic and cardiovascular involvement of COVID-19 causes thromboembolic events across multiple organs which mainly manifest as venous thromboembolism, and rarely, peripheral arterial thromboembolic events.… Click to show full abstract
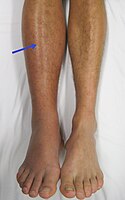
Background COVID-19 is a multi-systemic disorder. Hematologic and cardiovascular involvement of COVID-19 causes thromboembolic events across multiple organs which mainly manifest as venous thromboembolism, and rarely, peripheral arterial thromboembolic events. In-situ thrombosis of a healthy, non-atherosclerotic native artery is rare, and COVID-19 has been reported to be a cause of this phenomenon. We aimed to report our institutional experience with COVID-19 patients who developed acute limb ischemia (ALI) during hospitalization or after discharge. Methods This was a single-center cross-sectional study. Records of all patients ≥18 years of age admitted to a tertiary center with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 infection between September 1 and December 31, 2020 were retrospectively examined. Data regarding patient demographics, co-morbidities and outcomes were collected. Patients were followed-up during index hospitalization and for 30 days post-discharge. Acute limb ischemia was diagnosed by means of duplex ultrasound and computed tomography angiography in the presence of a clinical suspicion. Results A total of 681 consecutive patients (38.5% women) were hospitalized with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 during the study period. Median age was 63 years (IQR, 52-74). In-hospital mortality occurred in 94 (13.8%) patients. Ninety (13.2%) patients required intensive care unit admission at some point of their hospital stay. Six (0.9%) patients (one woman) with a median age of 62 years experienced ALI (IQR, 59-64.3). All patients were receiving low molecular weight heparin when they developed ALI. The median of duration between COVID-19 diagnosis and ALI symptom onset was 13 days (IQR, 11.3-14). Three patients underwent emergent surgical thrombectomy combined with systemic anticoagulation, and three received systemic anticoagulation alone. Two patients with ALI did not survive to hospital discharge. Among survivors, one patient underwent bilateral major amputations, and another underwent a minor amputation within one month of hospital discharge. Symptoms of ALI completely resolved in two patients without sequelae. Conclusion COVID-19 is a multi-systemic disorder with involvement of hematologic and cardiovascular systems. Despite widespread use of thromboprophylaxis, hospitalized patients with COVID-19 are at increased risk of ALI, and subsequent limb loss or even death.
Journal Title: Annals of Vascular Surgery
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!