Photo from wikipedia
The characteristics of neonatal immune cells display intrinsic differences compared with adult immune cells. Therefore, a comprehensive analysis of key gene expression regulation is required to understand the response of… Click to show full abstract
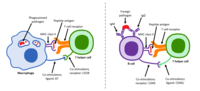
The characteristics of neonatal immune cells display intrinsic differences compared with adult immune cells. Therefore, a comprehensive analysis of key gene expression regulation is required to understand the response of the human fetal immune system to infections. Here, we applied single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) and single-cell sequencing assay for transposase-accessible chromatin (scATAC-seq) to systematically profile umbilical cord blood (UCB) nucleated cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) to identify their composition and differentially expressed genes. The immune cells in neonatal UCB demonstrated the expression of key genes, such as HBG2, NFKBIA, JUN, FOS, and TNFAIP3. In contrast, natural killer and T cells, which are constituents of adult PBMCs, exhibited high cytotoxic gene expression. Furthermore, we obtained similar results from the data of scATAC-seq by identifying the status of chromatin accessibility of key genes. Therefore, scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq of neonatal UCB nucleated cells and adult PBMCs could serve as an invaluable resource for elucidating the regulatory mechanisms of responses of distinct immune cell types and further identifying the differences between neonatal and adult immune responses to predict the potential underlying mechanism for neonatal immune tolerance.
Journal Title: Biochemical and biophysical research communications
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!