Photo from wikipedia
Abstract This paper reports mechanistic studies in ultrasound-assisted riboflavin production by wild strain of D. hansenii var. hansenii. Statistical optimization of fermentation resulted in riboflavin yield of 1.8 mg/g DCW. Supplementation… Click to show full abstract
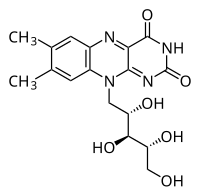
Abstract This paper reports mechanistic studies in ultrasound-assisted riboflavin production by wild strain of D. hansenii var. hansenii. Statistical optimization of fermentation resulted in riboflavin yield of 1.8 mg/g DCW. Supplementation of medium with glycine, Fe3+, cobalt and zinc further enhanced yield to 4.1 mg/g DCW. Intensification of fermentation by sonication (at 10% duty cycle) in four intervals of 12 h each (in total log phase of 48 h) was attempted. Sonication in final 12 h of log phase was most effective with the highest yield of 20 mg/g DCW. Kinetic analysis of the ultrasound-assisted fermentation revealed higher maximum specific growth rate of cells (0.30 h−1) with reduced Monod constant (5.67 g/L), indicating faster cell transport and higher substrate affinity. SDS-PAGE analysis of proteins involved in riboflavin metabolism showed overexpression of all proteins in ultrasound-assisted fermentation, which enhanced the metabolism. These results are attributed to intense microturbulence generated by sonication.
Journal Title: Bioresource Technology Reports
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!