Photo from wikipedia
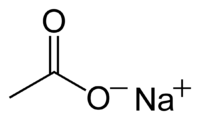
Abstract Mixed culture polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) production now-a-days attracts a lot of attention. A unified model of this process was developed that was calibrated and validated with independent experimental datasets. Ammonium‑nitrogen… Click to show full abstract
Abstract Mixed culture polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) production now-a-days attracts a lot of attention. A unified model of this process was developed that was calibrated and validated with independent experimental datasets. Ammonium‑nitrogen was one of control handle to maximize PHA production; increased PHA to active biomass ratio from 1.3 to 2.47. Elimination of non-PHA-producing bacteria was not significantly affected by more than two feast-famine cycles. Presence of acetate reduced PHA uptake for growth. PHA productivity was increased with increasing acetate feeding rate from 6.5 to 14.3 g-acetate/L/h but further increasing decreased PHA productivity due to high dilution and acetate inhibition. The best process alternative to maximize PHA production was a three steps process: feast-famine to eliminate non-PHA-producing organism, continuous feeding to enrich PHA-producing organism and then nitrogen stress for PHA production. However, PHA-producing organism never be in PHA free famine phase, it reduced the PHA to active biomass ratio from 2.47 to 1.97.
Journal Title: Bioresource Technology Reports
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!