Photo from academic.microsoft.com
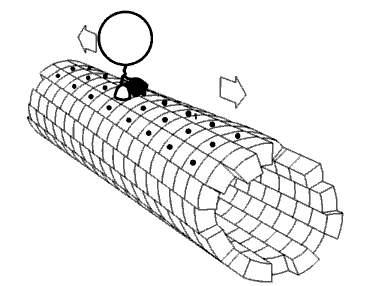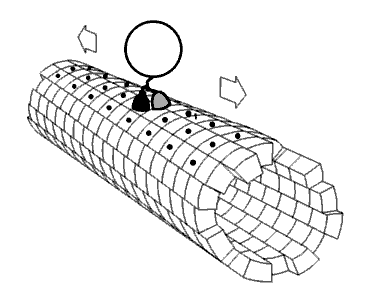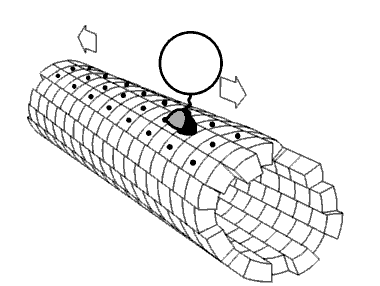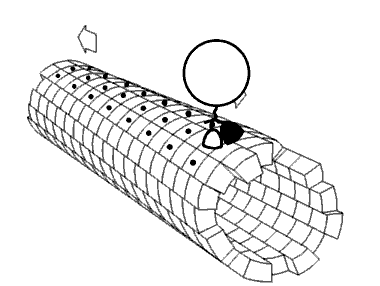
Mechanical interactions between a cell and its environment, or between cells, influence key developmental and physiologic processes as well as many aspect of disease (1,2). Indeed the ability of a… Click to show full abstract
Mechanical interactions between a cell and its environment, or between cells, influence key developmental and physiologic processes as well as many aspect of disease (1,2). Indeed the ability of a cell to sense, produce, and respond to mechanical cues has emerged as a fundamental regulator of cell behaviors such as differentiation, proliferation, survival, and migration. In mechanical terms the interactions governing these behaviors are regulated by intracellular and extracellular physical events that are orchestrated by complex biochemical and mechanical signals.
Journal Title: Biophysical journal
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!