Photo from wikipedia
Bone metastasis are the most common cause of pain related to cancer, reducing patients' quality of life, and sometimes threatening their life-expectancy. Their management has to be pluridisciplinary, because of… Click to show full abstract
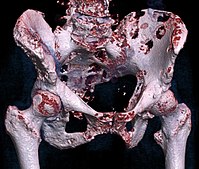
Bone metastasis are the most common cause of pain related to cancer, reducing patients' quality of life, and sometimes threatening their life-expectancy. Their management has to be pluridisciplinary, because of all the therapeutic options and the diversity of bone metastasis locations. The aim of this work is to propose a rational decisional algorithm for the treatment strategy of these secondary locations. Anti-resorbtive drugs with systemic action, surgery, conventional or stereotactic radiation therapy, and new techniques of interventional radiology are options that could be used separately or combined. They have shown benefits on symptomatic treatment, improving quality of life. Their indications vary according to the tumor site (short vs. long bones, carrier vs. non-carrier bones), the symptomatology (pain, neurologic symptoms), and the presence of complications (most of all fractures). The diverse presentations lead us to define this decisional algorithm, to guide the practice, while giving the maximal benefit to each patient according to each metastasis.
Journal Title: Bulletin du cancer
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!