Photo from wikipedia
Polyelectrolyte complexes (PECs) as safe drug delivery carriers, are spontaneously formed by mixing the oppositely charged polyelectrolyte solutions in water without using organic solvents nor chemical cross-linker or surfactant. Intensifying… Click to show full abstract
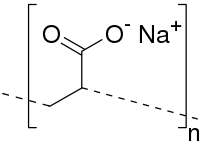
Polyelectrolyte complexes (PECs) as safe drug delivery carriers, are spontaneously formed by mixing the oppositely charged polyelectrolyte solutions in water without using organic solvents nor chemical cross-linker or surfactant. Intensifying attentions on the PECs study are aroused in academia and industry since the fabrication process of PECs is mild and they are ideal vectors for the delivery of susceptible drugs and macromolecules. Chitosan as the unique natural cationic polysaccharide, is a good bioadhesive material. Besides, due to its excellent biocompatibility, biodegradability, abundant availability and hydrophilic nature, chitosan-based PECs have been extensively applied for drug delivery, particularly after administration through mucosal and parenteral routes. The purpose of this review is to compile the recent advances on the biomedical applications of chitosan-based PECs, with specific focuses on the mucosal delivery, cancer therapy, gene delivery and anti-HIV therapy. The challenges and the perspectives of the chitosan-based PECs are briefly commented as well.
Journal Title: Carbohydrate polymers
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!