Photo from wikipedia
Advanced maternal age is highly associated with a decline in oocyte quality, but effective approaches to improve it have still not been fully determined. Here, we report that in vivo supplementation… Click to show full abstract
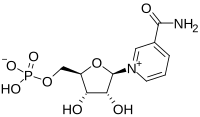
Advanced maternal age is highly associated with a decline in oocyte quality, but effective approaches to improve it have still not been fully determined. Here, we report that in vivo supplementation of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) efficaciously improves the quality of oocytes from naturally aged mice by recovering nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) levels. NMN supplementation not only increases ovulation of aged oocytes but also enhances their meiotic competency and fertilization ability by maintaining the normal spindle/chromosome structure and the dynamics of the cortical granule component ovastacin. Moreover, single-cell transcriptome analysis shows that the beneficial effect of NMN on aged oocytes is mediated by restoration of mitochondrial function, eliminating the accumulated ROS to suppress apoptosis. Collectively, our data reveal that NMN supplementation is a feasible approach to protect oocytes from advanced maternal age-related deterioration, contributing to the improvement of reproductive outcome of aged women and assisted reproductive technology.
Journal Title: Cell reports
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!