Photo from wikipedia
Summary Defining factors that govern CD8+ T cell immunodominance is critical for the rational design of vaccines for viral pathogens. Here, we assess the contribution of human leukocyte antigen (HLA)… Click to show full abstract
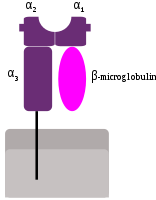
Summary Defining factors that govern CD8+ T cell immunodominance is critical for the rational design of vaccines for viral pathogens. Here, we assess the contribution of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class-I-peptide stability for 186 optimal HIV epitopes across 18 HLA alleles using transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP)-deficient mono-allelic HLA-expressing cell lines. We find that immunodominant HIV epitopes increase surface stabilization of HLA class-I molecules in comparison to subdominant epitopes. HLA class-I-peptide stability is also strongly correlated with overall immunodominance hierarchies, particularly for epitopes from high-abundance proteins (e.g., Gag). Moreover, HLA alleles associated with HIV protection are preferentially stabilized by epitopes derived from topologically important viral regions at a greater frequency than neutral and risk alleles. These findings indicate that relative stabilization of HLA class-I is a key factor for CD8+ T cell epitope immunodominance hierarchies, with implications for HIV control and the design of T-cell-based vaccines.
Journal Title: Cell Reports
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!