Photo from wikipedia
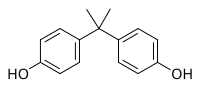
Bisphenol A (BPA), a contaminant of emerging concern, can affect plant root growth by changing various physiological processes. Mitochondria are critical organelles that produce energy for growth. However, how BPA… Click to show full abstract
Bisphenol A (BPA), a contaminant of emerging concern, can affect plant root growth by changing various physiological processes. Mitochondria are critical organelles that produce energy for growth. However, how BPA affects the function and ultrastructure of mitochondria and then plant root growth remains unclear. Here, we evaluated the lethality of BPA to root tip cells, investigated the energy production process of mitochondria, observed mitochondrial ultrastructure, and measured reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lipid peroxidation levels in mitochondria of soybean seedlings roots exposed to exogenous BPA. We found that low-dose BPA (1.5 mg/L) exposure induced limited toxicity in root tip cells, increased the activities of key enzymes (citrate synthase, succinate dehydrogenase, malate dehydrogenase and cytochrome C oxidase) involved in tricarboxylic acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, promoted adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthesis, and increased ROS production in mitochondria. Higher doses of BPA (6.0, 17.2 mg/L) exposure caused massive cell death in root tips, decreased the above key enzyme activities and ATP production, and destroyed mitochondrial ultrastructure; meanwhile, these doses also significantly increased mitochondrial ROS and membrane lipid peroxidation levels. In conclusion, we found that mitochondria were significant subcellular sites through which BPA can damage plant roots. BPA-induced excessive ROS destroyed mitochondrial ultrastructure and inhibited key enzyme activities in energy production, resulting in decreased ATP synthesis and cell death in root tips. Our results demonstrated the effects of BPA on mitochondrial function and structure in plant root cells, providing new insights into understanding the underlying mechanisms of BPA affecting plant root growth.
Journal Title: Chemosphere
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!