Photo from wikipedia
This study presents a one-step synthetic approach for magnetic biochar (MBC) photo-degradation of diethyl phthalate (DEP). The results showed that MBC exhibited better catalytic property for DEP degradation than BC,… Click to show full abstract
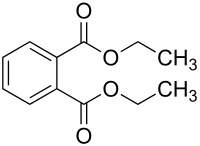
This study presents a one-step synthetic approach for magnetic biochar (MBC) photo-degradation of diethyl phthalate (DEP). The results showed that MBC exhibited better catalytic property for DEP degradation than BC, and its catalytic performance was influenced by the amount of Fe doping. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR), quenching experiments, and chemical probe studies confirmed the presence of persistent free radicals (PFRs), hydroxyl radicals (·OH), and superoxide anion radical (·O2-) in both of BC and MBC. Solar light promoted the formation of PFRs in BC system, which transferred electrons to oxygen to form ·O2-, thus yielding ·OH. On the other hand, electron transfer occurred between PFRs and Fe3+ for MBC, Fe2+ played an important role in activation of O2 and ·O2- production. Subsequently, photo-Fenton reaction was primarily responsible for ·OH formation. This work compared the different generation pathways for ROS between BC and MBC and provides new insight into the possible mediatory roles of BC in O2 activation under solar light by transition metals.
Journal Title: Chemosphere
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!