Photo from wikipedia
Abstract Chitin, one of the most abundant natural polymers, is easy-accessible, biodegradable, and biocompatible. However, its poor solubility in common solvents limited its applications. In this paper, we used ionic… Click to show full abstract
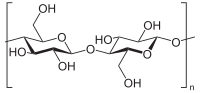
Abstract Chitin, one of the most abundant natural polymers, is easy-accessible, biodegradable, and biocompatible. However, its poor solubility in common solvents limited its applications. In this paper, we used ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-metlimidazolium acetate ([BMIM]Ac) to dissolve chitin, and then prepared the ionic liquid gels and regenerated hydrogels (ionic liquid replaced by 6 M KOH). In particular, the rheological properties were investigated for the ionic liquid gels of chitin, and the application of corresponding regenerated hydrogels as the supercapacitor was explored. It was found that the chain rigidity of chitin and the hydrogen bonds between chitin and [BMIM]Ac affected greatly the rheological behavior of chitin/[BMIM]Ac gels. Moreover, a supercapacitor could be assembled using the regenerated chitin hydrogel as polymer electrolyte, and exhibited a higher capacitance and better cyclic behavior when compared to a commercial membrane.
Journal Title: Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!