Photo from wikipedia
In order for a pregnancy to successfully deliver at term, there are three main mechanical ‘compartments’ (the uterus, cervix, amniotic sac) that must engage in a well-orchestrated symbiotic relationship to… Click to show full abstract
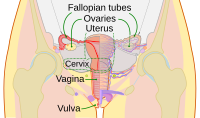
In order for a pregnancy to successfully deliver at term, there are three main mechanical ‘compartments’ (the uterus, cervix, amniotic sac) that must engage in a well-orchestrated symbiotic relationship to house the growing fetus until it is ready for delivery. Traditionally, the cervix was considered a passive bystander in the process of parturition because it was thought to be mostly a collagenous structure that somehow remodeled under the growing weight of the pregnancy and dilated due to the force of labor contractions to allow for delivery of the fetus. Recently, an updated paradigm of cervical tissue structure has emerged, which states there is a significant amount of functional smooth muscle at the top of the cervix (the area of the internal os) that is circumferentially oriented around the periphery of the endocervical canal and that this smooth muscle body may form a specialized sphincter. Given that the smooth muscle in the cervix is connected to the smooth muscle in the uterus, this review explores new concepts, in which this potential sphincter may participate in activating the uterus to contract leading to normal or abnormal labor.
Journal Title: Current Opinion in Physiology
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!