Photo from wikipedia
Children with major congenital anomalies often require lifelong access to health and social care services. Estimating future numbers of affected individuals can aid health and social care planning. This study… Click to show full abstract
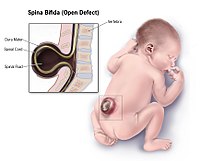
Children with major congenital anomalies often require lifelong access to health and social care services. Estimating future numbers of affected individuals can aid health and social care planning. This study aimed to estimate the number of children aged 0-15 years living with spina bifida or Down syndrome in England and Wales by 2020. Cases of spina bifida and Down syndrome born during 1998-2013 were identified from the Northern Congenital Abnormality Survey and the National Down Syndrome Cytogenetic Register, respectively. The number of infants born with spina bifida during 1998-2019 were estimated by applying the average prevalence rate in the North of England to actual and projected births in England and Wales. Poisson regression was performed to estimate the number of infants born with Down syndrome in England and Wales during 1998-2013 and 2004-2019. The numbers of children aged 0-15 living with spina bifida or Down syndrome in 2014 and in 2020 were then estimated by multiplying year- and age-specific survival estimates by the number of affected births. An estimated 956 children with isolated spina bifida, 623 children with spina bifida and hydrocephalus and 11,592 children with Down syndrome aged 0-15 years will be living in England and Wales by 2020, increases of 7.2%, 12.0% and 12.7% since 2014, respectively. Due to improvements in survival, an increase in population size and changes in maternal age distribution at delivery, we anticipate further increases in the number of children living with spina bifida or Down syndrome by 2020.
Journal Title: European journal of medical genetics
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!