Photo from wikipedia
This is the first study to investigate the extent of reduction in acrylamide formation during baking with the addition of (-)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) extracted from green tea, and to determine… Click to show full abstract
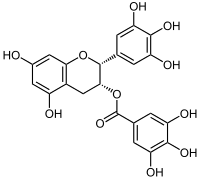
This is the first study to investigate the extent of reduction in acrylamide formation during baking with the addition of (-)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) extracted from green tea, and to determine whether EGCG influences the texture and colour attributes of bread, or interacts with other ingredients. EGCG powders were added to white bread formulations at the concentrations of 3.3, 6.6 and 9.9g·kg-1. The amount of acrylamide in the bread was analysed using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. EGCG addition significantly reduced the acrylamide formation by 37% compared to the control and decreased the moisture content of the bread by 6%. It did not affect its texture attribute, but increased the lightness and the yellowness and decreased the redness of bread crust (with contrasting results in crumb). It also decreased granule size and porosity. In conclusion, EGCG fortification is a feasible method to decrease acrylamide formation in baked bread.
Journal Title: Food chemistry
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!