Photo from wikipedia
Abstract When considering sensory discrimination studies, multiple d-prime values are often obtained from several sensory attributes. In this paper, we introduce principal component analysis as a way of gaining information… Click to show full abstract
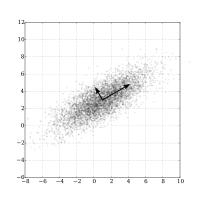
Abstract When considering sensory discrimination studies, multiple d-prime values are often obtained from several sensory attributes. In this paper, we introduce principal component analysis as a way of gaining information about d-prime values across sensory attributes. Specifically, we propose estimating d-prime values using a Thurstonian mixed model for binary paired comparison data and then using these estimates in a principal component analysis. Binary paired comparisons are a sensitive way to test products with only subtle differences. When analyzing data with a Thurstonian mixed model, product-specific as well as assessor-specific d-prime values are obtained. Principal component analysis of these values results in information about products and assessors across multiple sensory attributes illustrated by product and attribute maps. Furthermore, the analysis captures individual differences. Thus, by using d-prime values from a multi-attribute 2-AFC study in principal component analysis insights that are typically obtained considering quantitative descriptive analysis are obtained.
Journal Title: Food Quality and Preference
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!