Photo from wikipedia
Serum mast cell tryptase is used to support the diagnosis of anaphylaxis. The recommended clinical cut-off for total tryptase ( Click to show full abstract
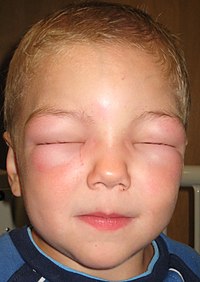
Serum mast cell tryptase is used to support the diagnosis of anaphylaxis. The recommended clinical cut-off for total tryptase (<11.4μg/L) appears unsuitable in the post mortem setting due to largely unknown processes which result in significantly elevated levels in these samples. Consequently there is no widely accepted tryptase cut-off level for diagnosing an anaphylactic death. This 5-year retrospective study compared total tryptase levels in post mortem femoral blood in anaphylactic deaths and control. Univariate and multivariate analysis was used to assess the relative contribution of other factors (age, gender, post mortem interval, and presence of resuscitation) on post mortem tryptase levels. Nine anaphylactic deaths and 45 controls were identified. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis identified an optimal cut-off of 53.8μg/L, with sensitivity of 89%, and specificity of 93%, for total post mortem tryptase in femoral blood to diagnosis anaphylaxis. No other factors showed any statistical significant contribution to post mortem tryptase elevation. Femoral total post mortem tryptase level of 53.8μg/L and above is a useful ancillary test in diagnosing an anaphylactic death.
Journal Title: Forensic science international
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!