Photo from wikipedia
Abstract Fatigue damage and consequent failure account for the majority of the failure in metallic bolted joints of aerospace and mechanical engineering applications. In this paper, we present a cumulative… Click to show full abstract
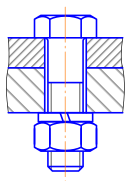
Abstract Fatigue damage and consequent failure account for the majority of the failure in metallic bolted joints of aerospace and mechanical engineering applications. In this paper, we present a cumulative fatigue damage evaluation approach for metallic bolted joints based on a combined continuum damage mechanics (CDM) theory and the critical plane approach. The analysis approach is applicable to both proportional and non-proportional multiaxial loading conditions. A cycle jumping based algorithm with a fixed damage evolution rate is adopted for efficient numerical approximation. To further increase the computational efficiency, a simplified modeling strategy is developed to avoid the expensive calculation of the full loading-unloading cyclic stress history. The proposed approach is established based on the assumption that a linear relation can be established between the minimum and maximum stress tensors in high-cycle fatigue analysis and is thus only dependent on the maximum stress states. A set of examples including a notched specimen and a metallic bolted joint with pre-tension are simulated to demonstrate the simplified approach.
Journal Title: International Journal of Fatigue
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!