Photo from wikipedia
INTRODUCTION Traumatic brain injury associated coagulopathy is frequent, either in isolated traumatic brain injury in civilian practice and in combat traumatic brain injury. In war zone, it is a matter… Click to show full abstract
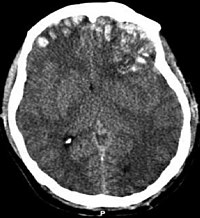
INTRODUCTION Traumatic brain injury associated coagulopathy is frequent, either in isolated traumatic brain injury in civilian practice and in combat traumatic brain injury. In war zone, it is a matter of concern because head and neck are the second most frequent site of wartime casualty burden. Data focusing on transfusion requirements in patients with war related TBI coagulopathy are limited. MATERIALS AND METHODS A descriptive analysis was conducted of 77 penetrating traumatic brain injuries referred to a French role 3 medical treatment facility in Kabul, Afghanistan, deployed on the Kabul International Airport (KaIA), over a 30 months period. RESULTS On 77 patients, 23 died during the prehospital phase and were not included in the study. Severe traumatic brain injury represented 50% of patients. Explosions were the most common injury mechanism. Extracranial injuries were present in 72% of patients. Traumatic brain injury coagulopathy was diagnosed in 67% of patients at role 3 admission. Red blood cell units (RBCu) were transfused in 39 (72%) patients, French lyophilized plasma (FLYP) in 41 (76%), and fresh whole blood (FWB) in 17 (31%). CONCLUSION The results of this study support previous observations of coagulopathy as a frequent complication of traumatic brain injury. The majority of patients with war related penetrating traumatic brain injury presented with extracranial lesions. Most of them required a high level of transfusion capacity.
Journal Title: Injury
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!