Photo from wikipedia
To reduce dependence on petroleum, the biosynthesis of important chemicals from simple substrates using industrial microorganisms has attracted increased attention. Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae offers a sustainable and flexible… Click to show full abstract
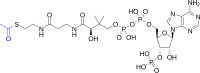
To reduce dependence on petroleum, the biosynthesis of important chemicals from simple substrates using industrial microorganisms has attracted increased attention. Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae offers a sustainable and flexible alternative for the production of various chemicals. As a key metabolic intermediate, malonyl-CoA is a precursor for many useful compounds. However, the productivity of malonyl-CoA derivatives is restricted by the low cellular level of malonyl-CoA and enzymatic performance. In this review, we focused on how to increase the intracellular malonyl-CoA level and summarize the recent advances in different metabolic engineering strategies for directing intracellular malonyl-CoA to the desired malonyl-CoA derivatives, including strengthening the malonyl-CoA supply, reducing malonyl-CoA consumption, and precisely controlling the intracellular malonyl-CoA level. These strategies provided new insights for further improving the synthesis of malonyl-CoA derivatives in microorganisms.
Journal Title: Journal of biotechnology
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!