Photo from wikipedia
GA: granuloma annulare GGA: generalized granuloma annulare PDE-4: phosphodiesterase 4 Th: T helper INTRODUCTION Generalized granuloma annulare (GGA) is a widespread inflammatory condition that is often resistant to current treatment… Click to show full abstract
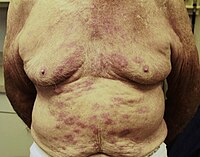
GA: granuloma annulare GGA: generalized granuloma annulare PDE-4: phosphodiesterase 4 Th: T helper INTRODUCTION Generalized granuloma annulare (GGA) is a widespread inflammatory condition that is often resistant to current treatment modalities. Apremilast, a phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE-4) inhibitor, may represent a novel treatment option due to its ability to downregulate inflammatory pathways while maintaining a favorable safety profile. We report 2 cases of GGA treated with apremilast. Granuloma annulare (GA) is a relatively common benign inflammatory skin condition. The generalized variant, defined as involving the trunk and extremities, makes up one-fourth of cases. Localized GA often spontaneously resolves; however, GGA is likely to persist despite therapy. Presently, there are no controlled clinical trials suggesting an optimal treatment, and current therapies are based on case reports and expert opinion. Apremilast is an oral PDE-4 inhibitor approved for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, and recently approved for oral ulcers associated with Behçet disease. The exact pathogenesis of GA is unknown, but it is believed to be a type 1 T helper (Th1)-type delayed hypersensitivity reaction to a variety of antigens. Apremilast may be used as a treatment in GA due the ability to reduce Th1 cytokines such as tumor necrosis factora and interferon-g. In the following cases, the use of apremilast as a potential treatment for GGA is assessed.
Journal Title: JAAD Case Reports
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!