Photo from wikipedia
Abstract An intensified method for treatment of wastewater containing a commercial dye (Methyl Violet 2B (MV 2B)) has been studied with novel approaches based on UV-air bubble induced oxidation. A… Click to show full abstract
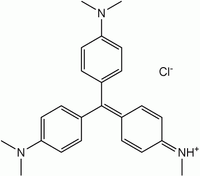
Abstract An intensified method for treatment of wastewater containing a commercial dye (Methyl Violet 2B (MV 2B)) has been studied with novel approaches based on UV-air bubble induced oxidation. A modified reactor containing small glass balls was used for this purpose. The impact of the operating parameters such as initial concentration and pH as well as the effect of loadings of various catalysts likeTiO2, MnO2, ZnO etc. on the extent of removal of MV 2B dye have been investigated. So as to maximize the efficacy of removal of the dye, the reactor used in the author’s earlier work was modified by incorporating ultraviolet light source in the system. The removal of Methyl Violet (2B) was found to be maximum (96.8%) with the loading of a mixture of TiO2 and MnO2 catalysts. Also, the effect of various metal oxide catalysts on the removal of methyl violet 2B has been observed in the order of TiO2 > MnO2 > ZnO. Overall, the present investigation established that hybrid processes with the use of optimized loading of catalysts have promising future and can be successfully applied for the removal of toxic dyes from aqueous solution with intensification benefits.
Journal Title: Journal of environmental chemical engineering
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!