Photo from wikipedia
Abnormal orientation of the T-wave axis and increased angle between the QRS complex (depolarization) and the T-wave (repolarization) have long been assumed to provide a global measure of repolarization abnormality,… Click to show full abstract
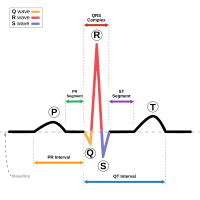
Abnormal orientation of the T-wave axis and increased angle between the QRS complex (depolarization) and the T-wave (repolarization) have long been assumed to provide a global measure of repolarization abnormality, and have been used to assess ventricular repolarization. The ability of the T wave axis deviation and the QRS-T angle to predict incident coronary heart events was examined in several studies. However, conflicting results have led to significant controversy in the literature concerning their purported ability. Potential explanations involve true variation between study populations, non-standardized cut-off values, different baseline cardiovascular risk levels or different patterns of confounding by other concomitant cardiovascular risk factors. In the present article we will attempt to briefly present the rationale and pathophysiology behind these indices, summarize existing knowledge regarding their prognostic significance and their correlation with established cardiovascular disease risk factors. Further prospective studies are necessary to confirm or refute whether T-wave axis deviation, QRS-T angle and ventricular gradient may in the future serve as indicators of incident coronary heart events and mortality, both in populations with higher prevalence of subclinical advanced atherosclerotic heart disease and in apparently healthy subjects.
Journal Title: Journal of electrocardiology
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!