Photo from wikipedia
Episodes of frequent flooding continue to increase, often causing serious damage and tools to identify areas affected by such disasters have become indispensable in today's society. Using the latest techniques… Click to show full abstract
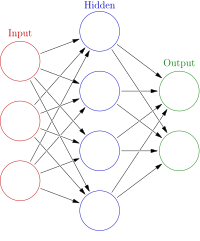
Episodes of frequent flooding continue to increase, often causing serious damage and tools to identify areas affected by such disasters have become indispensable in today's society. Using the latest techniques can make very accurate flood predictions. In this study, we introduce four effective methods to evaluate the flood susceptibility of Poyang County, in China, by integrating two independent models of frequency ratio and index of entropy with multilayer perceptron and classification and regression tree models. The flood locations of the study area were identified through the flood inventory process, and 12 flood conditioning factors were used in the training and validation processes. According to the results of the linear support vector machine, elevation, slope angle, and soil have the highest predictive ability. The experimental results of the four hybrid models demonstrate that between 20% and 50% of the study area has high and very high flood susceptibility. The multilayer perceptron-probability density hybrid model is the most effective among the six comparative methods.
Journal Title: Journal of environmental management
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!