Photo from wikipedia
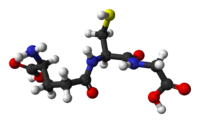
Abstract Acute alcoholic liver injury (AALI) refers to the inflammatory hepatic damage caused by alcohol. In severe cases, it can lead to steatohepatitis, alcoholic fibrosis and even cirrhosis. In this… Click to show full abstract
Abstract Acute alcoholic liver injury (AALI) refers to the inflammatory hepatic damage caused by alcohol. In severe cases, it can lead to steatohepatitis, alcoholic fibrosis and even cirrhosis. In this study, we analyzed the hepatoprotective activity of L-theanine on mice fed with a large amount of ethanol at one time, and the underlying molecular mechanism. The extensive liver injury caused by alcohol feeding was alleviated by L-theanine, which reduced tissue damage, decreased transaminase levels, and increased antioxidant activity. Mechanistically, L-theanine downregulated phosphorylated NF-κB, TNF-α and IKKα in the liver tissues and the LO2 normal hepatocyte cell line, which in turn lowered secretion of iNOS, IL-1β and IL-6. Taken together, L-theanine prevents alcohol-induced liver inflammation by blocking the intrahepatic TNF-α/NF-κB pathway, and is a promising treatment strategy against AALI.
Journal Title: Journal of Functional Foods
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!