Photo from wikipedia
Series sulfur-doped TiO2/amine-functionalized zirconium metal organic frameworks (S-TiO2/UiO-66-NH2) composites (U1Tx) were facilely fabricated from the as-prepared S-TiO2 and UiO-66-NH2 via ball-milling method. The photocatalytic activities of U1Tx toward Cr(VI) reduction… Click to show full abstract
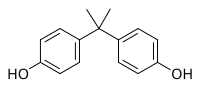
Series sulfur-doped TiO2/amine-functionalized zirconium metal organic frameworks (S-TiO2/UiO-66-NH2) composites (U1Tx) were facilely fabricated from the as-prepared S-TiO2 and UiO-66-NH2 via ball-milling method. The photocatalytic activities of U1Tx toward Cr(VI) reduction and bisphenol A (BPA) degradation were tested under low-power LED visible light. The results demonstrated that U1T3 exhibited better photocatalytic performances than the pristine S-TiO2 and UiO-66-NH2 due to the improved separation and migration of electrons and holes. Furthermore, the influence factors like pH values and foreign ions on the photocatalytic performances of U1Tx were also investigated. The Box-Behnken design methodology was utilized to further clarify that the inorganic foreign anions and dissolved organic matters could exert significant effects on photocatalytic Cr(VI) reduction performance. As well, the possible pathway of BPA degradation was depicted. After four runs of Cr(VI) removal, it was found that U1T3 exhibited preferable reusability and water stability. The probable reaction mechanism was proposed and verified by active species capture experiments, electron spin resonance determination and electrochemical analyses.
Journal Title: Journal of hazardous materials
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!