Photo from wikipedia
Abstract Nanocomposite membranes consisting of silver nanoparticles dispersed in ionic liquid such as 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate (BMIM+BF4−) were prepared and tested for the separation of olefin/paraffin mixtures. Here, we report the… Click to show full abstract
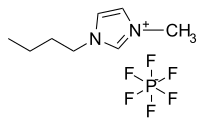
Abstract Nanocomposite membranes consisting of silver nanoparticles dispersed in ionic liquid such as 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate (BMIM+BF4−) were prepared and tested for the separation of olefin/paraffin mixtures. Here, we report the effects of high temperature heat treatment on the dispersion of silver nanoparticles in ionic liquids and their separation performance for propylene/propane mixtures. When a 1:0.2 weight ratio of BMIM+BF4−/Ag metal composite membrane was heated at 100 ℃, both the selectivity and the mixed gas permeance increased from 8.2 to 17 and from 0.8 to 1.1 GPU, respectively. The enhanced separation performance is attributable to the increased surface area of the silver nanoparticles resulting from the disentanglement of nanoparticles by the interactions between the particle surfaces and the ionic liquid. The average particle size of disentangled silver nanoparticles is about 5 nm, as confirmed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). FT-Raman and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) also demonstrated favorable interactions between the silver nanoparticle surfaces and the counter anions of the ionic liquid. The influence of heat treatment on Ag particle dispersion in ionic liquid was studied by small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) analysis.
Journal Title: Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!