Photo from wikipedia
Abstract Cr3C2, TaC and VC are the most widely used grain growth inhibitors (GGIs) in cemented carbides. The inhibition effectiveness and the formation of brittle carbides by over-doping these GGIs… Click to show full abstract
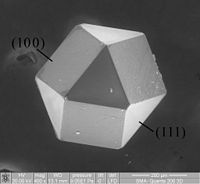
Abstract Cr3C2, TaC and VC are the most widely used grain growth inhibitors (GGIs) in cemented carbides. The inhibition effectiveness and the formation of brittle carbides by over-doping these GGIs are closely associated with their solubilities in the binder phase. A series of WC-Ni-based “model alloys” with high content of binder phase and different dopants of GGIs have been designed based on thermodynamic calculations and then prepared through conventional powder metallurgy method. The subsequent microstructures and the solubilities of GGIs in Ni binder phase were characterized by means of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and wavelength-dispersive electron-probe microanalysis (WDS-EPMA), respectively. The thermodynamic description of the fcc phase (Ni binder phase) has been remodeled according to the presently obtained experimental data. A good agreement between experimental data and thermodynamic calculations can be obtained, which can provide a theoretical basis to the development of WC-Ni-based cemented carbides.
Journal Title: Journal of materials research and technology
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!