Photo from wikipedia
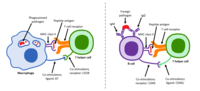
Abstract Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a disease with autoimmune etiology. The main pathomechanism is related to the production of antibodies against nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AChR) located in the postsynaptic membrane.… Click to show full abstract
Abstract Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a disease with autoimmune etiology. The main pathomechanism is related to the production of antibodies against nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AChR) located in the postsynaptic membrane. The present study is set to compare the serum level of interleukin-33 (IL-33)/receptor ST2 in patients with myasthenia gravis and controls; and to study the relation with the severity of disease. Our observations confirm that a significant increase in serum concentrations of IL-33 and ST2 was observed in MG patients compared to healthy individuals. This relation is not precisely known yet, which requires more studies.
Journal Title: Journal of Neuroimmunology
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!