Photo from wikipedia
OBJECTIVE To quantify the cross-sectional area (CSA) of lumbar dorsal root ganglion (DRG) by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and investigate the relationship between the cross-sectional area (CSA) of DRGs and… Click to show full abstract
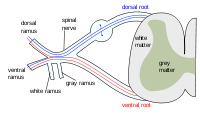
OBJECTIVE To quantify the cross-sectional area (CSA) of lumbar dorsal root ganglion (DRG) by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and investigate the relationship between the cross-sectional area (CSA) of DRGs and sensory nerve action potentials (SNAP) amplitude in the lower extremities. METHODS Thirty-eight DRGs (20 L5 roots and 18 S1 roots) in 10 adult subjects were reviewed retrospectively. The CSA of the DRG was calculated from MR images of the coronal plane. SNAP amplitudes of the superficial peroneal nerve and sural nerve were corresponded to L5 and S1-DRGs. RESULTS The mean CSA of DRGs was 66.6 ± 13.7 mm2 in L5-DRG and 79.5 ± 14.3 mm2 in S1-DRG. The means of SNAP amplitudes were 19.6 ± 6.2 μV in superficial peroneal nerves and 24.6 ± 9.0 μV in sural nerves. In multivariate regression analysis, the CSA of DRGs had a significant correlation with SNAP amplitude. CONCLUSION The area of L5 and S1-DRGs may be positively correlated with SNAP amplitude.
Journal Title: Journal of Clinical Neuroscience
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!