Photo from wikipedia
INTRODUCTION Regenerative endodontic procedures (REPs) are intended to repair and regenerate part of the pulp-dentin complex. The aim of this study was to systematically appraise existing evidence on the effectiveness… Click to show full abstract
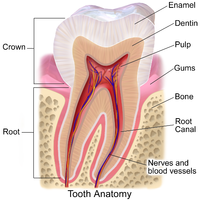
INTRODUCTION Regenerative endodontic procedures (REPs) are intended to repair and regenerate part of the pulp-dentin complex. The aim of this study was to systematically appraise existing evidence on the effectiveness of REPs on mature teeth with pulp necrosis and apical periodontitis. METHODS Electronic database and hand searches were implemented on 8 databases of published and unpublished literature from inception to January 3, 2021, for the identification of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) or prospective clinical trials. Related keywords included: "regenerative", "pulp revascularization", "revitalization procedure", "necrotic mature teeth". Random effects meta-analysis was conducted assessing as main outcome treatment success. Risk of bias was assessed through the Cochrane RoB 2.0 tool and the quality of the evidence was assessed with the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE). RESULTS Of 337 initial hits, four RCTs were eligible for inclusion, while 3 were included in the quantitative synthesis. Overall, there was no difference in the relative risk (RR) for successful/ unsuccessful treatment outcome between either REPs or conventional treatment (3 studies, RR= 1.03; 95% Confidence Interval: 0.92, 1.15; p=0.61; heterogeneity I-squared: 0.0%, p=0.53; Prediction Interval: 0.51, 2.09). Risk of bias ranged from low to raising some concerns, while the quality of the evidence was graded as moderate. CONCLUSIONS Based on moderate quality evidence, REPs appear as a viable treatment alternative for mature necrotic teeth with periapical lesions, at present. Further, well-designed RCTs might also provide confirmatory evidence in this respect, while also frame a backbone for standardization of the therapeutic protocol of REPs.
Journal Title: Journal of endodontics
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!