Photo from wikipedia
Graphical abstract Figure. No Caption available. HighlightsA stable and accurate method was developed for colistin quantification from DBS.On‐spot internal standard addition was applied for accurate quantification.DBS provides benefit of stability… Click to show full abstract
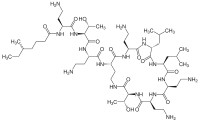
Graphical abstract Figure. No Caption available. HighlightsA stable and accurate method was developed for colistin quantification from DBS.On‐spot internal standard addition was applied for accurate quantification.DBS provides benefit of stability for easily hydrolyzed colistin prodrug.Only 3.6% of the prodrug hydrolyzed in DBS at room temperature after 48 h. Abstract Outbreaks of multidrug‐resistant Gram‐negative bacterial infections have been reported worldwide. Colistin, an antibiotic with known nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity, is now being used to treat multidrug‐resistant Gram‐negative strains. In this study, we applied an on‐spot internal standard addition approach coupled with an ultra high‐performance liquid chromatography‐tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) method to quantify colistin A and B from dried blood spots (DBSs). Only 15 &mgr;L of whole blood was required for each sample. An internal standard with the same yield of extraction recoveries as colistin was added to the spot before sample extraction for accurate quantification. Formic acid in water (0.15%) with an equal volume of acetonitrile (50:50 v/v) was used as the extraction solution. With the optimized extraction process and LC–MS/MS conditions, colistin A and B could be quantified from a DBS with respective limits of quantification of 0.13 and 0.27 &mgr;g mL−1, and the retention times were < 2 min. The relative standard deviations of within‐run and between‐run precisions for peak area ratios were all < 17.3%. Accuracies were 91.5‐111.2% for lower limit of quantification, low, medium, and high QC samples. The stability of the easily hydrolyzed prodrug, colistin methanesulfonate, was investigated in DBSs. Less than 4% of the prodrug was found to be hydrolyzed in DBSs at room temperature after 48 h. The developed method applied an on‐spot internal standard addition approach which benefited the precision and accuracy. Results showed that DBS sampling coupled with the sensitive LC–MS/MS method has the potential to be an alternative approach for colistin quantification, where the bias of prodrug hydrolysis in liquid samples is decreased.
Journal Title: Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!