Photo from wikipedia
The underlying pathophysiological mechanisms involved in cerebral aneurysms rupture remain unclear. This study was performed to investigate the differentially expressed proteins between ruptured and unruptured aneurysms using quantitative proteomics. The… Click to show full abstract
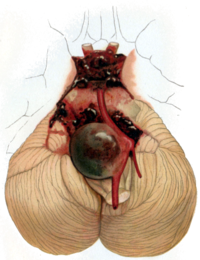
The underlying pathophysiological mechanisms involved in cerebral aneurysms rupture remain unclear. This study was performed to investigate the differentially expressed proteins between ruptured and unruptured aneurysms using quantitative proteomics. The aneurysmal walls of six ruptured aneurysms and six unruptured aneurysms were collected during the surgical operation. The isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantification (iTRAQ) were used to identify the differentially expressed proteins and western blotting was performed to validate the expression of the proteins of interest. Bioinformatics analysis of the differentially expressed proteins was also performed using the KEGG database and GO database. Between ruptured and unruptured aneurysms, 169 proteins were found differently expressed, including 74 up-regulated proteins and 95 down-regulated proteins with a fold change ≥ 2 and p value ≤ .05. KEGG pathway analysis revealed that phagosome, focal adhesion and ECM-receptor interaction were the most common pathways involved in aneurysm rupture. In addition, the differential expressions of ITGB3, CRABP1 and S100A9 were validated by western blotting. Through the iTRAQ method, we found that inflammatory responses and cell-matrix interactions may play a significant role in the rupture of cerebral aneurysms. These findings provide a basis for better understanding of pathophysiological mechanisms associated with aneurysm rupture. BIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE Intracranial aneurysm is the leading cause of life-threating subarachnoid hemorrhage which can cause 45% patients die within 30 days and severe morbidity in long-term survivors. With a high prevalence ranging from 1% to 5% in general population, cerebral aneurysm has become a widespread health hazard over past decades. Though great advances have been achieved in the diagnosis and treatment of this disease, the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms of aneurysm rupture remains undetermined and a lot of uncertainty still exists surrounding the treatment of unruptured cerebral aneurysms. Clarifying the mechanism associated with aneurysm rupture is important for estimating the rupture risk, as well as the development of new treatment strategy. Some previous studies have analyzed the molecular differences between ruptured and unruptured IAs at gene and mRNA levels, but further comprehensive proteomic studies are relatively rare. Here we performed a comparative proteomics study to investigate the differentially expressed proteins between ruptured IAs (RIAs) and unruptured IAs (UIAs). Results of our present study will provide more insights into the pathogenesis of aneurysm rupture at protein level. With a better understanding of pathophysiological mechanisms associated with aneurysm rupture, some noninvasive treatment strategies may be developed in the future.
Journal Title: Journal of proteomics
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!