Photo from wikipedia
Villitis of unknown etiology (VUE) is characterized by lympho-histiocytic infiltrates, which are predominant within the villous stroma. VUE can be of low grade i.e. affecting less than 10 contiguous villi… Click to show full abstract
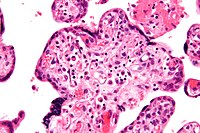
Villitis of unknown etiology (VUE) is characterized by lympho-histiocytic infiltrates, which are predominant within the villous stroma. VUE can be of low grade i.e. affecting less than 10 contiguous villi or high grade with either patchy or diffuse subgroups (the later concerning more than 30 % of distal villi). Several other placental lesions could be associated with VUE, in particular in diffuse subgroups, such as diffuse perivillous fibrin deposition and chronic intervillositis. One of the most characteristic features of VUE is the late onset of fetal growth restriction after 32 weeks of gestation, and earlier detection of villitis should first raise an infectious origin. High grade VUE has been associated with fetal growth restriction, prematurity, fetal deaths, recurrent pregnancy loss, central nervous system injury and is characterized by relatively high risk of recurrence (25-50 %). Prospective and well-designed studies are necessary to determine the real prevalence of these adverse pregnancy events associated with VUE. Data about the management of VUE are extremely scarce and thus no recommendation based on the literature review could be actually done.
Journal Title: Journal of reproductive immunology
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!