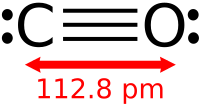
Photo from wikipedia
Abstract CO oxidative coupling to dimethyl oxalate (DMO) on Pd(100), (110) and (211) surfaces have been investigated through the density functional theory (DFT) method together with periodic slab models. Effect… Click to show full abstract
Abstract CO oxidative coupling to dimethyl oxalate (DMO) on Pd(100), (110) and (211) surfaces have been investigated through the density functional theory (DFT) method together with periodic slab models. Effect of different surface structures on adsorption, reaction and catalytic activity has been explored. CO at different adsorption sites participated in the oxidative coupling reaction according to the surface structure. CO at bridge or hollow site was consumed for the coupling reaction on the Pd(100) surface, and the favorable route was COOCH3-COOCH3 coupling path. While CO-COOCH3 coupling route was the optimal on Pd(110) and (211) surfaces, CO at top and bridge site took part in the reaction, respectively. Pd(100) surface exhibited higher catalytic activity and selectivity to DMO than Pd(110) and (211) surfaces.
Journal Title: Molecular Catalysis
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!