Photo from wikipedia
Neurodegenerative disorders are gaining ever more importance in ageing populations of animals and people. Altered insulin signaling and type II diabetes have been linked to the development of Alzheimer's disease… Click to show full abstract
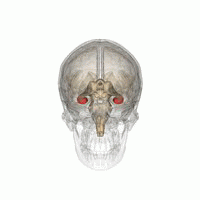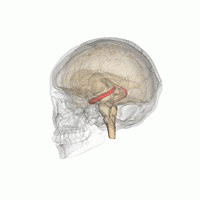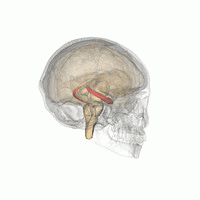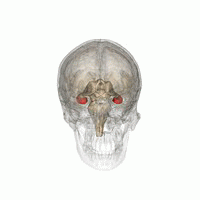
Neurodegenerative disorders are gaining ever more importance in ageing populations of animals and people. Altered insulin signaling and type II diabetes have been linked to the development of Alzheimer's disease (AD) in humans and AD-like neurodegeneration in other long-lived animals. Donkeys are unusual amongst domestic species for their exceptional longevity and are additionally predisposed to abnormalities of insulin metabolism similar to those found in humans. In this study, the parietal lobe and hippocampus of 13 aged (>30 years) and 2 younger control donkeys were evaluated immunohistologically for the presence, distribution, and frequency of neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) and amyloid plaques (AP); the characteristic lesions of AD. AP were in parietal cortices of 9 donkeys, with a predilection for deep sulci, and NFT-like structures were observed in 7 donkeys, primarily within cortical areas. No changes were observed in the control donkeys. This represents the first identification of both AP and NFT in equids and is a stimulus for future work assessing their metabolic status in parallel.
Journal Title: Neurobiology of Aging
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!