Photo from wikipedia
OBJECTIVE Health care disparities, often of an obscure nature, result in African American women (AAw) having enhanced risk of adverse cardiovascular events. Therefore, we sought to determine the prevalence of… Click to show full abstract
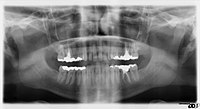
OBJECTIVE Health care disparities, often of an obscure nature, result in African American women (AAw) having enhanced risk of adverse cardiovascular events. Therefore, we sought to determine the prevalence of calcified carotid artery atheromas (CCAA), a validated risk indicator of these events, on their digital panoramic images. STUDY DESIGN Comprehensive electronic medical records and digital panoramic images of self-identified AAw aged ≥45 years treated between 2007 and 2014 were retrieved from a Veterans Affairs Dental Service. Images were reviewed for CCAA in the cervical bifurcation region, and medical records were reviewed for atherogenic risk factors: hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia. RESULTS The study sample of 171 AAw (mean age 58.2 ± 8.0 years) evidenced a 24% CCAA positive prevalence rate. In comparison with the CCAA negative group, those with atheromas were significantly older (61.4 ± 10.1 vs. 57.2 ± 7.0), diabetic, and dyslipidemic. Also observed among the full study sample was significant concordant increase of CCAA prevalence with age. Among those who were CCAA positive, there was a significant increased prevalence of dyslipidemia with age. CONCLUSIONS Panoramic images of older AAw frequently revealed carotid atheromas, a risk indicator of generalized atherosclerosis and future adverse cardiovascular events.
Journal Title: Oral surgery, oral medicine, oral pathology and oral radiology
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!