Photo from wikipedia
Abstract Random lasing in a lotus leaf, with a wide tunable spectrum from planar liquid waveguide gain channels is described. The lotus leaf shows multiple scattering from the micro-papilla and… Click to show full abstract
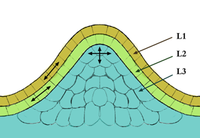
Abstract Random lasing in a lotus leaf, with a wide tunable spectrum from planar liquid waveguide gain channels is described. The lotus leaf shows multiple scattering from the micro-papilla and nanoscale coralloid tomentum on its surface. The Fraunhofer diffraction pattern demonstrates excellent coherence and directionality for our random laser. The emission spectrum wavelength can be tuned by changing the pump position due to the random distribution of the micro/nano-scale features on the lotus leaf. Potential applications of the random laser include probing micro/nano-scale structural alterations, optical biosensors on chips, and developing a multi-color random laser.
Journal Title: Organic Electronics
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!