Photo from wikipedia
Abstract Late Devonian plant remains, species of Archaeopteris and Sublepidodendron , and some representative miospores, are recognized from silty mudstone borehole core (well depth: 2063.1–2068.8 m) in the southern Yellow Sea,… Click to show full abstract
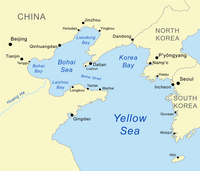
Abstract Late Devonian plant remains, species of Archaeopteris and Sublepidodendron , and some representative miospores, are recognized from silty mudstone borehole core (well depth: 2063.1–2068.8 m) in the southern Yellow Sea, China. These plants have been thoroughly studied and are widely distributed in the Upper Devonian of southern China. The plant-fossil-bearing borehole core correlates to the Upper Devonian (Famennian) terrestrial to shallow-marine Wutung Formation of southern China, lower Yangtze Plate. Moreover, the Late Devonian megaplant and miospore records palaeogeographically distinguish the Sino-Korean and Yangtze Plates. The northeastern boundary of the Yangtze Plate is discussed. It is proposed that the northeastern end of the Yangtze Plate probably extends to the Imjingang Belt and the Gyeonggi Massif, the central part of the Korean Peninsula.
Journal Title: Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!