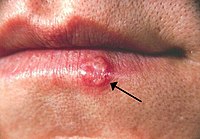
Photo from wikipedia
OBJECTIVE Therefore, we conducted a systematic review to evaluate the efficacy of PDT in the management of RHL. STUDY DESIGN systematic review. METHODS This study was reported according to the… Click to show full abstract
OBJECTIVE Therefore, we conducted a systematic review to evaluate the efficacy of PDT in the management of RHL. STUDY DESIGN systematic review. METHODS This study was reported according to the PRISMA checklist and we performed a literature search on five databases. RESULTS The search revealed that there are no published clinical trials addressing PDT on RHL, therefore we conducted a review of case reports and five studies were included for qualitative review. The number of treated patients varied from 2 to 6 in each article. Most studies used methylene blue as a photosensitizer, while one used 5-aminolevulinic acid. For light irradiation, most studies used laser and one used a red light from halogen lamp. Patients' follow-up varied from 24 hours to 12 months. All articles reported good outcomes with resolution of disease and no recurrences. Only one study reported adverse effects during treatment (burning and pain). CONCLUSION The results of this review suggest that PDT could be an effective treatment for herpes labialis. However, due to very few case reports and heterogeneity among protocols, there is a call for well-designed randomized clinical trials to confirm the efficacy of this therapy and to establish standardized protocols. The review protocol was registered at the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) under number CRD CRD42018108973.
Journal Title: Photodiagnosis and photodynamic therapy
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!