Photo from wikipedia
Wound healing usually follows a predictable sequence and prognosis of events. Its evolutionary process is the result of a complicated interaction between patient-related factors, the wound, the treatment used and… Click to show full abstract
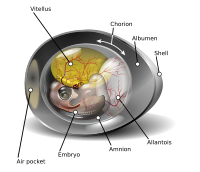
Wound healing usually follows a predictable sequence and prognosis of events. Its evolutionary process is the result of a complicated interaction between patient-related factors, the wound, the treatment used and the skills and knowledge of the professionals who treat them. Only through a meticulous initial assessment of the wound is it possible to identify the factors that contribute to its complexity. The challenge for professionals will be to implement efficient therapies at the right time and in the most cost-efficient way in order to reduce associated problems, treat the symptoms and expectations of the patients and achieve adequate wound healing whenever possible. This is particularly evident in big chronic wounds with considerable tissue loss, which become senescent in the process of inflammation or proliferation losing the ability to epithelialize. Generally, chronic wounds do not respond to current treatments, therefore they need special interventions. AM is a tissue of particular interest as a biological dressing and it has well-documented reepithelialization effects which are in part related to its capacity to synthesize and release biological active factors. Our studies have demonstrated that amniotic membrane (AM) is able to induce epithelialization in chronic wounds that were unable to epithelialize. AM induces several signaling pathways that are involved in cell migration and/or proliferation. Additionally, AM is able to selectively antagonize the anti-proliferative effect of transforming growth factor-ß (TGF-β) by modifying the genetic program that TGF-β induces on keratinocytes. The combined effect of AM on keratinocytes, promoting cell proliferation/migration and antagonizing the effect of TGF-β is the perfect combination, allowing chronic wounds to move out of their non-healing state and progress into epithelialization.
Journal Title: Placenta
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!