Photo from wikipedia
Abstract Investigations of spin-crossover in an iron(II) tris(diimine) system, based on the ligands L1 (4,5-dimethy-2-(pyridine-2-yl)imidazole) and L2 (1-acetic ethyl-2-(pyridine-2-yl)-imidazole), have been presented in this paper. The methyl groups at adjacent… Click to show full abstract
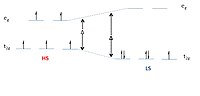
Abstract Investigations of spin-crossover in an iron(II) tris(diimine) system, based on the ligands L1 (4,5-dimethy-2-(pyridine-2-yl)imidazole) and L2 (1-acetic ethyl-2-(pyridine-2-yl)-imidazole), have been presented in this paper. The methyl groups at adjacent sites to the donor atoms in the ligand L1 generated the crossover situation for complexes Fe(L1)3(ClO4−)2 (1), Fe(L1)3(BF4−)2 (2), Fe(L1)3(PF6−)2 (3) and Fe(L1)3(SbF6−)2 (4), while the acetic ethyl group at the non-coordinating NH site of the ligand L2 resulted in an increase in the ligand field and generated a low-spin (LS) state for the complex Fe(L2)3(ClO4−)2 (5). Complexes 1 and 5 were structurally characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction at different spin-states, while the phase purity of complexes 2–4 was confirmed by PXRD. Raman, IR and UV–Vis absorption spectra and magnetic properties of 1–4 were obtained, which revealed the influence of different counter anions on the spin transition temperatures. The blue-shift of IR and Raman spectra, red-shift and decrease in molar absorptivity of UV–Vis absorption spectra all follow the sequence 1
Journal Title: Polyhedron
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!