Photo from wikipedia
Abstract Multi-angle modulation properties of electrolyte gated graphene visible-infrared modulators with supercapacitor structures have been examined in both experiment and theory. Both transmission and reflection geometries have been studied, and… Click to show full abstract
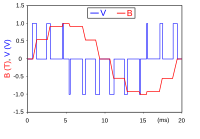
Abstract Multi-angle modulation properties of electrolyte gated graphene visible-infrared modulators with supercapacitor structures have been examined in both experiment and theory. Both transmission and reflection geometries have been studied, and the results show that all the modulations of these devices are gate voltage and wavelength dependent. Maximum modulation depths for transmission device ∼3% and reflection modulator ∼5% are obtained, which can be attributed to the electrolyte assistant considerable change of the Fermi energy with tunable gate voltage. Moreover, little incident angle dependency can be observed with a certain gate voltage. Theoretical analysis based on the different tangential and normal optical responses of the quartz/graphene/eletrolyte interface has been used to explain the phenomena, which indicated a common effect of p -polarized and s -polarized light. This work offers useful insight into a multi-angle application of the graphene-based optical modulator in visible-infrared region.
Journal Title: Solid-state Electronics
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!