Photo from wikipedia
Implantable medical devices are an integral part of primary/critical care. However, these devices carry a high risk for blood clots, caused by platelet aggregation on a foreign body surface. This… Click to show full abstract
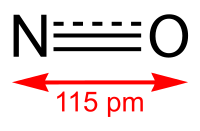
Implantable medical devices are an integral part of primary/critical care. However, these devices carry a high risk for blood clots, caused by platelet aggregation on a foreign body surface. This study focuses on the development of a simplified approach to create nitric oxide (NO) releasing intravascular electrochemical oxygen (O2) sensors with increased biocompatibility and analytical accuracy. The implantable sensors are prepared by embedding S-nitroso-N-acetylpenacillamine (SNAP) as the NO donor molecule in the walls of the catheter type sensors. The SNAP-impregnated catheters were prepared by swelling silicone rubber tubing in a tetrahydrofuran solution containing SNAP. Control and SNAP-impregnated catheters were used to fabricate the Clark-style amperometric PO2 sensors. The SNAP-impregnated sensors release NO under physiological conditions for 18 d as measured by chemiluminescence. The analytical response of the SNAP-impregnated sensors was evaluated in vitro and in vivo. Rabbit and swine models (with sensors placed in both veins and arteries) were used to evaluate the effects on thrombus formation and analytical in vivo PO2 sensing performance. The SNAP-impregnated PO2 sensors were found to more accurately measure PO2 levels in blood continuously (over 7 and 20 h animal experiments) with significantly reduced thrombus formation (as compared to controls) on their surfaces.
Journal Title: Talanta
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!