Photo from wikipedia
Abstract The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of prebiotic fibres on appetite-regulating hormones, subjective feeling of appetite and energy intake in subjects with type 2 diabetes.… Click to show full abstract
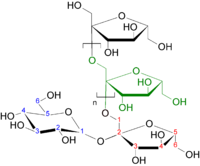
Abstract The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of prebiotic fibres on appetite-regulating hormones, subjective feeling of appetite and energy intake in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Data presented are secondary outcomes of a study investigating the effect of prebiotics on glucagon-like peptide-1 and glycaemic regulation. We conducted a randomised and placebo-controlled crossover trial to evaluate the effects of 16 g/d of inulin-type fructans or a control supplement (maltodextrin) for 6 weeks in randomised order, with a 4-week washout period in-between, on appetite in thirty-five men and women with type 2 diabetes. Data were collected at visits before and after each treatment: plasma concentration of the satiety-related peptides ghrelin and peptide YY (PYY) were assessed during a standardised mixed meal. The subjective sensation of appetite was evaluated in response to an ad libitum lunch by rating the visual analogue scale. Twenty-nine individuals (twelve women) were included in the analyses. Compared to control treatment, the prebiotics did not affect ghrelin (P =0⋅71) or the ratings of hunger (P = 0⋅62), satiety (P = 0⋅56), fullness (P = 0⋅73) or prospective food consumption (P = 0⋅98). Energy intake also did not differ between the treatments. However, the response of PYY increased significantly after the control treatment with mean (sem) 11⋅1 (4⋅3) pg/ml when compared to the prebiotics −0⋅3 (4⋅3) pg/ml (P = 0⋅013). We observed no effect of inulin-type fructans on appetite hormones, subjective feeling of appetite or energy intake in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Journal Title: Journal of Nutritional Science
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!