Photo from wikipedia
Abstract The mammary gland, a unique exocrine organ, is responsible for milk synthesis in mammals. Neonatal growth and health are predominantly determined by quality and quantity of milk production. Amino… Click to show full abstract
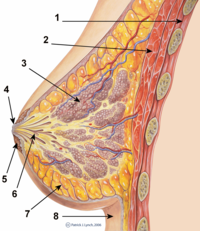
Abstract The mammary gland, a unique exocrine organ, is responsible for milk synthesis in mammals. Neonatal growth and health are predominantly determined by quality and quantity of milk production. Amino acids are crucial maternal nutrients that are the building blocks for milk protein and are potential energy sources for neonates. Recent advances made regarding the mammary gland further demonstrate that some functional amino acids also regulate milk protein and fat synthesis through distinct intracellular and extracellular pathways. In the present study, we discuss recent advances in the role of amino acids (especially branched-chain amino acids, methionine, arginine and lysine) in the regulation of milk synthesis. The present review also addresses the crucial questions of how amino acids are transported, sensed and transduced in the mammary gland.
Journal Title: Nutrition Research Reviews
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!