Photo from wikipedia
ABSTRACT The first half of the Mississippian or Early Carboniferous (Tournaisian to mid- Viséan), an interval of about 20 million years, has become known as “Romer's Gap” because of its… Click to show full abstract
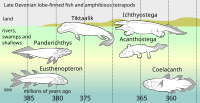
ABSTRACT The first half of the Mississippian or Early Carboniferous (Tournaisian to mid- Viséan), an interval of about 20 million years, has become known as “Romer's Gap” because of its poor tetrapod record. Recent discoveries emphasise the differences between pre-“Gap” Devonian tetrapods, unambiguous stem-group members retaining numerous “fish” characters indicative of an at least partially aquatic lifestyle, and post-“Gap” Carboniferous tetrapods, which are far more diverse and include fully terrestrial representatives of the main crown-group lineages. It seems that “Romer's Gap” coincided with the cladogenetic events leading to the origin of the tetrapod crown group. Here, we describe a partial right lower jaw ramus of a tetrapod from the late Tournaisian or early Viséan of Scotland. The large and robust jaw displays a distinctive character combination, including a significant mesial lamina of the strongly sculptured angular, an open sulcus for the mandibular lateral line, a non-ossified narrow Meckelian exposure, a well-defined dorsal longitudinal denticle ridge on the prearticular, and a mesially open adductor fossa. A phylogenetic analysis places this specimen in a trichotomy with Crassigyrinus and baphetids + higher tetrapods in the upper part of the tetrapod stem group, above Whatcheeria, Pederpes, Ossinodus, Sigournea and Greererpeton. It represents a small but significant step in the gradual closure of “Romer's Gap”.