Photo from wikipedia
The use of alginate nanofibers in certain biomedical applications, including targeted delivery to the gut, is limited because an ethanol-free, biocompatible cross-linking method has not been demonstrated. Here, we developed… Click to show full abstract
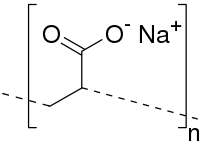
The use of alginate nanofibers in certain biomedical applications, including targeted delivery to the gut, is limited because an ethanol-free, biocompatible cross-linking method has not been demonstrated. Here, we developed water-stable, alginate-based nanofibers by systematically exploring post-electrospinning cross-linking approaches that used calcium ions dissolved in (1) a glycerol/water cosolvent system and (2) acidic, neutral, or basic aqueous solutions. Scanning electron microscopy proved that the fibers cross-linked in a glycerol cosolvent or pH-optimized solutions had maintained the same morphology as the ethanol-based literature control. Notably, cross-linked fibers were generally smaller in diameter than the as-spun fibers due to both chemical interactions and mass loss during cross-linking, which was supported by mass measurements, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis. During stability tests wherein the cross-linked fibers were exposed to three aqueous solutions, the cross-linked fibers were stable in water and acid buffer yet swelled in phosphate buffer saline, making them useful scaffolds for pH-controlled release applications. Proof-of-concept release experiments were conducted using a simulated gastrointestinal tract model. As desired, the cargo remained encapsulated within the cross-linked nanofibers when exposed to an acidic solution that modeled the stomach. Upon exposure to a solution that mimicked the intestines, the cargo was released. We suggest that these cross-linked, alginate-based nanofiber mats hold the potential to be broadly used in biomedical and environmental applications.
Journal Title: Biomacromolecules
Year Published: 2023
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!