Photo from wikipedia
Monitoring biodiversity is essential to assess the impacts of increasing anthropogenic activities in marine environments. Traditionally, marine biomonitoring involves the sorting and morphological identification of benthic macro-invertebrates, which is time-consuming… Click to show full abstract
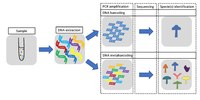
Monitoring biodiversity is essential to assess the impacts of increasing anthropogenic activities in marine environments. Traditionally, marine biomonitoring involves the sorting and morphological identification of benthic macro-invertebrates, which is time-consuming and taxonomic-expertise demanding. High-throughput amplicon sequencing of environmental DNA (eDNA metabarcoding) represents a promising alternative for benthic monitoring. However, an important fraction of eDNA sequences remains unassigned or belong to taxa of unknown ecology, which prevent their use for assessing the ecological quality status. Here, we show that supervised machine learning (SML) can be used to build robust predictive models for benthic monitoring, regardless of the taxonomic assignment of eDNA sequences. We tested three SML approaches to assess the environmental impact of marine aquaculture using benthic foraminifera eDNA, a group of unicellular eukaryotes known to be good bioindicators, as features to infer macro-invertebrates based biotic indices. We found similar ecological status as obtained from macro-invertebrates inventories. We argue that SML approaches could overcome and even bypass the cost and time-demanding morpho-taxonomic approaches in future biomonitoring.
Journal Title: Environmental science & technology
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!