Photo from wikipedia
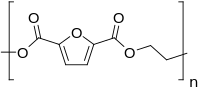
Poly(ethylene 2,5-furandicarboxylate) (PEF) is considered today as a very promising biobased polymer for packaging applications. Most often, scientific literature describes synthetic procedures based on the transesterification of the dimethylester of… Click to show full abstract
Poly(ethylene 2,5-furandicarboxylate) (PEF) is considered today as a very promising biobased polymer for packaging applications. Most often, scientific literature describes synthetic procedures based on the transesterification of the dimethylester of the 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid, whereas this paper aims at studying the possibility of a practical and profitable synthetic route for PEF comprising a direct esterification stage of 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid. In that respect two catalysts, zinc acetate and aluminum acetylacetonate, chosen for their compatibility with food contact applications and for featuring a potentially reduced environmental impact, were investigated. The synthesis was performed by using tight reaction conditions: low excess of diol and short reaction time. Interesting results were obtained in terms of final PEF viscosity, color, and diethylene glycol content, that may strongly influence thermal and barrier properties. Furthermore, the obtained amorphous polymers are potentially suitable...
Journal Title: Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!